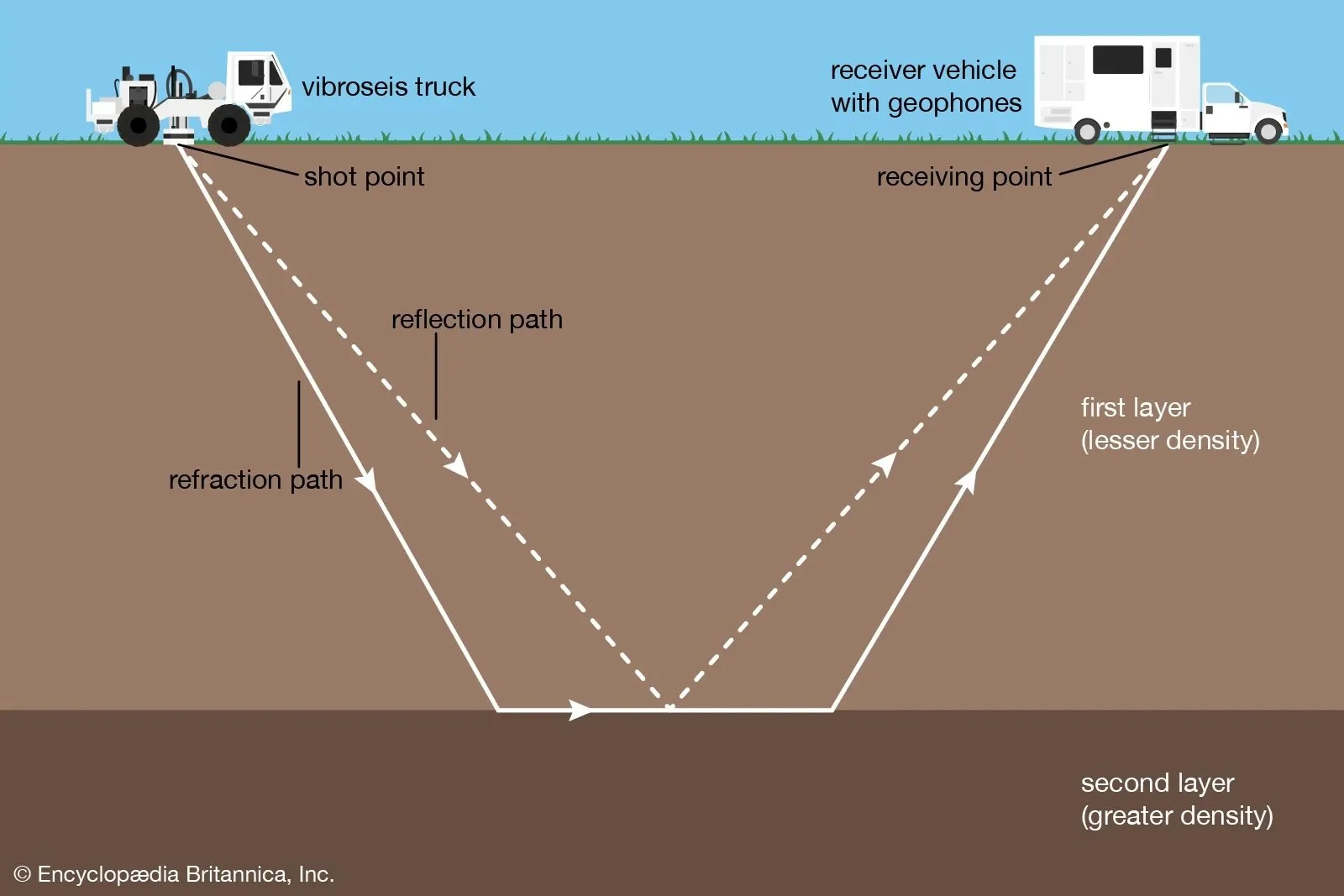
Seismic Refraction
Involves the generation and transmission of sound waves into the subsurface where it is then refracted or reflected at the interface between rocks with different physical properties or rocks that contain different fluid types
Measuring: mechanical response of rock and rock masses
MAGNETIC SURVEY
Magnetic readings are made with special equipment that logs the relative strength of the magnetic field at various points in a computer for analysis.
Measuring: identify mineralization based on magnetic signatures
GRAVITY SURVEY
Use of precise instruments to measure the strength of gravity at various locations
Most effective for : diamonds, rare mineralsFeature 1
Measuring: density
Magnetotellurics (MT)
Use of natural electromagnetic signals to image subsurface electrical conductivity structure through electromagnetic induction.
Measuring: resistivity as a function of depth
Electrical Resistivity Tomography (ERT)
Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR)
GPR enables the emission of electromagnetic (EM) waves and characterizes the material properties based on the reflected electromagnetic signal
Measuring: Material Properties
Ground Resistivity Mapping (GRM)
Use of electrodes embedded or integrated on the ground
Measuring: Resistivity
Induced Polarization (IP)
IP measurements can be acquired using the same four-electrode geometry that is conventionally used for electrical resistivity surveys, although IP surveys typically employ nonpolarizing electrodes.
Measuring: chargeability of the ground